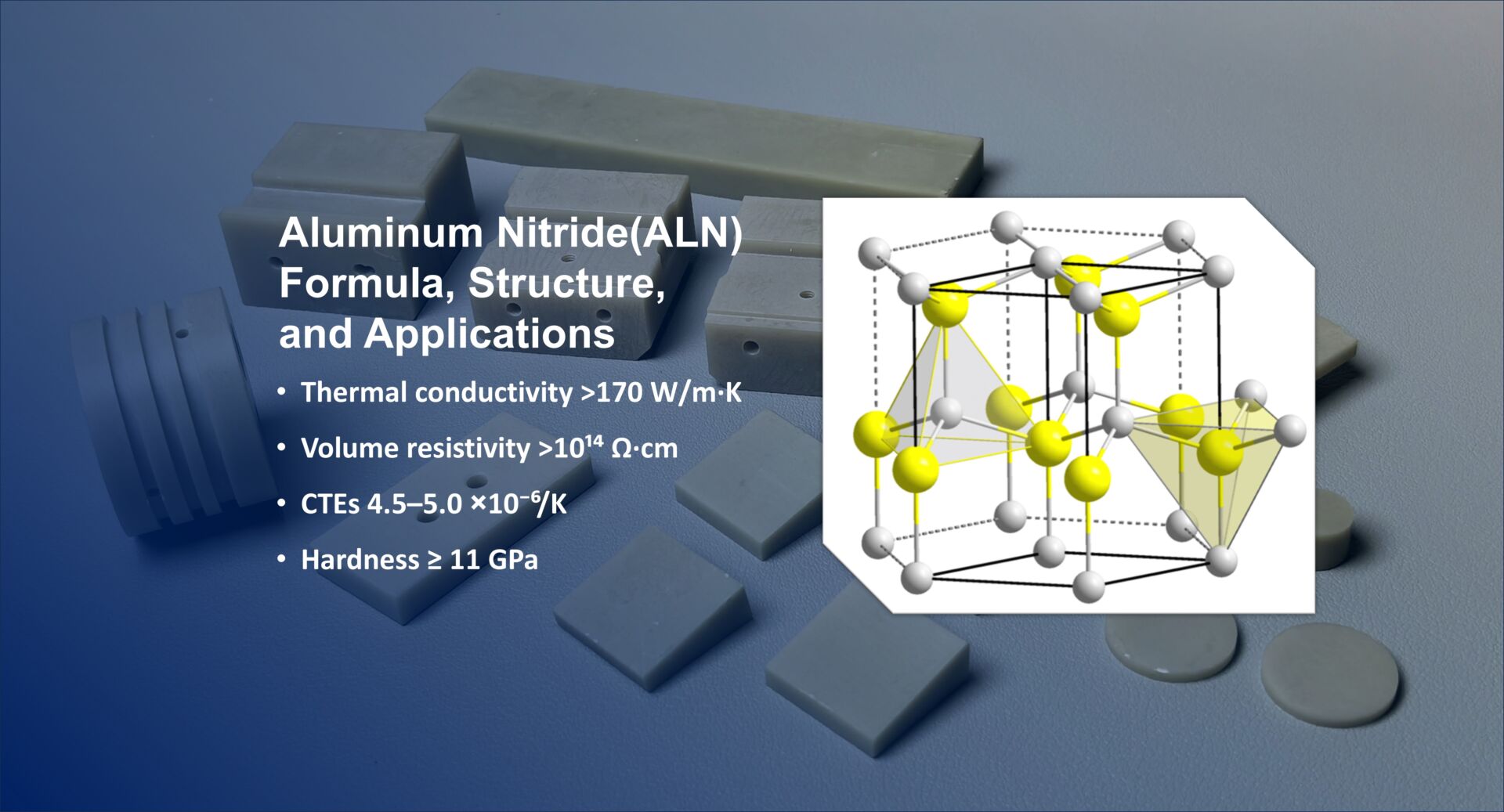
Introduction
Aluminum Nitride Ceramics (AlN Ceramics) are widely used in electronic packaging and high-power devices due to their high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation properties. However, during production, it is often observed that AlN ceramic plates from the same batch exhibit color differences. This article aims to demonstrate that these color differences do not affect the performance of AlN ceramics and that the differences are primarily due to variations in the cooling process.

Source of Color Differences: Influence of the Cooling Process
In the production of AlN ceramics, the post-sintering cooling stage is crucial. The temperature gradient and cooling rate during this process can impact the appearance of the ceramics. The primary factors contributing to color differences are:
Cooling Rate: Rapid cooling may cause microcracks or stress concentrations on the ceramic surface, altering the reflection and scattering of light, making the surface appear darker. Conversely, slower cooling results in a more uniform and lighter color.
Temperature Gradient: During the sintering process, the temperature gradient within the furnace can lead to uneven cooling, causing color differences.
Atmospheric Variations: Minor changes in the cooling atmosphere, such as differences in oxygen content, can lead to slight chemical reactions on the ceramic surface, affecting its color.
Impact of Color Differences on AlN Ceramics Performance
Although color differences are visible, extensive research and practical applications show that these differences are mainly surface phenomena and have minimal impact on the performance of AlN ceramics:
Thermal Conductivity: The cooling rate differences primarily affect the surface layer of the ceramics, while the thermal conductivity of AlN ceramics is mainly determined by their internal structure. The temperature gradient and cooling rate during the cooling process do not significantly alter the crystalline structure and density of the ceramics, thus having minimal impact on thermal conductivity.
Mechanical Strength: While the cooling rate may induce surface stress, these stresses are usually minor and concentrated on the surface layer, not significantly affecting overall mechanical strength. The flexural strength and impact resistance of AlN ceramics are primarily dependent on their overall structure and density, rather than surface color.
Electrical Insulation Performance: The color differences are due to surface cooling rate variations and do not substantially affect the electrical insulation performance of the ceramics. The electrical insulation properties of AlN ceramics are mainly determined by material purity and internal structure, which are not significantly influenced by the cooling process.
Surface Performance: Variations in cooling rates may slightly affect the surface hardness and wear resistance of the ceramics, but this impact is generally minor and can be mitigated through subsequent surface treatment processes such as polishing or coating.
Supporting Experimental Data
To further demonstrate that color differences do not significantly impact AlN ceramics performance, the following experimental data can be referenced:
Thermal Conductivity Tests: Thermal conductivity tests on AlN ceramic plates of different colors from the same batch show that the differences in thermal conductivity are within the margin of error, indicating that color differences do not significantly affect thermal conductivity.
Mechanical Strength Tests: Flexural strength tests on ceramic plates of different colors show no significant differences in strength values, confirming that color differences do not impact mechanical strength.
Electrical Insulation Performance Tests: Dielectric strength tests on ceramic plates of different colors show that all samples meet design requirements with no significant differences, demonstrating that color differences do not affect electrical insulation performance.
Conclusion
In summary, the color differences in AlN ceramic plates from the same batch are primarily caused by temperature gradients and variations in cooling rates during the cooling process. These color differences are only surface phenomena and do not significantly impact the thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, or electrical insulation performance of AlN ceramics. Therefore, color differences do not affect the practical performance of AlN ceramics. During production and quality control, more attention should be paid to the consistency of process parameters to ensure high quality and reliability of the products.