Aluminum Nitride Sheet Manufacturing Process
Aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic plates are widely used in high-end fields such as high-power electronic packaging, semiconductor heat dissipation substrates, and radio frequency devices due to their excellent thermal conductivity (170~230 W/(m·K)), high electrical insulation, and excellent mechanical properties.
Although hot pressing and isostatic pressing are suitable for preparing high-performance aluminum nitride sheets, they have problems such as high cost and low production efficiency. In order to solve this problem, Great Ceramic uses tape casting to prepare high-performance aluminum nitride ceramic sheets. (Tape casting is the main molding process for ALN sheets used in the electronics industry.)

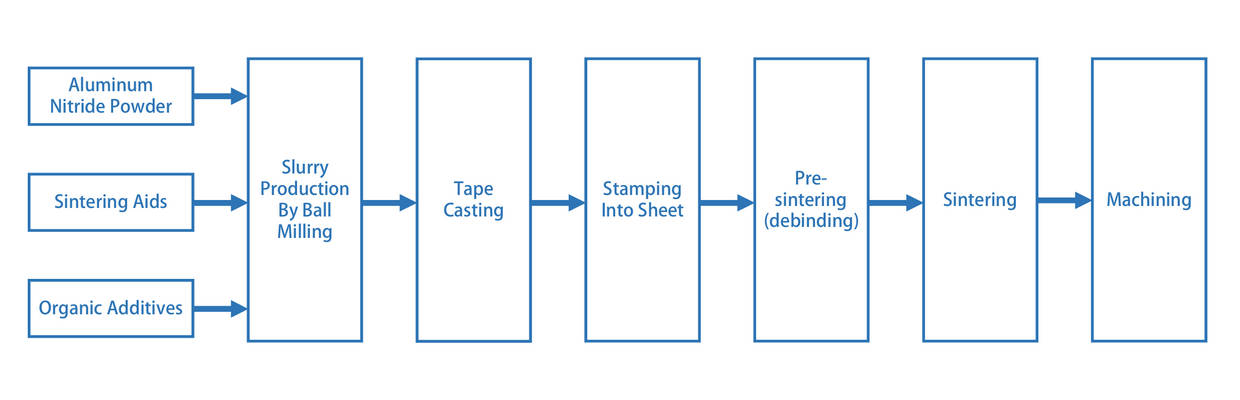
AlN sheet production process diagram

1. Raw material preparation: the cornerstone of substrate performance
In order to prepare aluminum nitride slurry with good fluidity, aluminum nitride powder, sintering aids (such as yttrium oxide, Y2O3), organic solvents (such as ethanol, toluene), binders and dispersants are fully mixed and ground in a ball mill.
In this process, the addition of organic mixed solvents, dispersants, binders and plasticizers is to give the slurry good tape casting properties. Among them, yttrium oxide (Y2O3) as a sintering aid can promote the densification of materials under normal pressure sintering conditions.
The viscosity of the slurry is an important factor affecting the performance of the final substrate. The key factors affecting viscosity include:
- Grinding time: The length of grinding time will directly affect the dispersion of the powder and the viscosity of the slurry.
- The amount of organic mixed solvent: The proportion of solvents will change the fluidity of the slurry.
- The amount of dispersant: The dispersant helps to evenly disperse the powder and avoid agglomeration.
- The amount of binder and plasticizer: These additives affect the formability and strength of the slurry.
Therefore, the formulation selection and process control of the slurry are crucial to the performance of aluminum nitride ceramic substrates.
2. Sheet forming: shaping the substrate
Tape casting has become a key technology for mass production of aluminum nitride ceramic substrates due to its high production efficiency and easy to achieve continuous and automated production. This process can not only significantly reduce production costs, but also flexibly control the thickness of the substrate, from ultra-thin substrates below 10µm to thick substrates above 1mm.
Compared with other molding processes, tape casting has many advantages:
- Continuous production;
- The product has small defects and stable performance;
- Suitable for industrial production;
- Suitable for the preparation of large thin plate ceramic parts
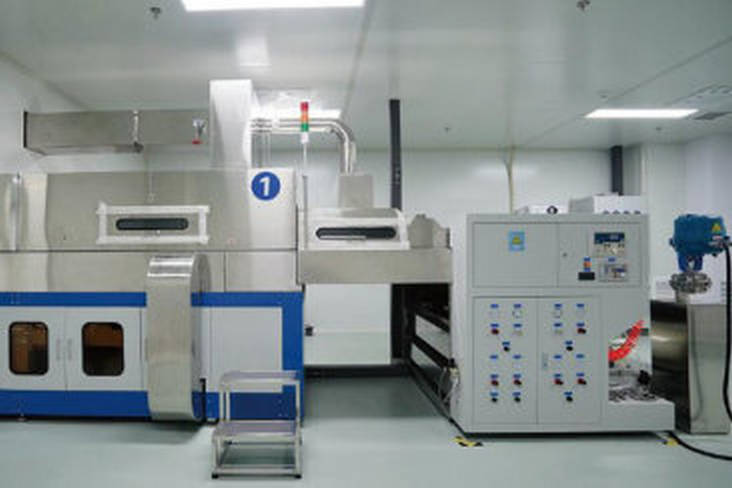
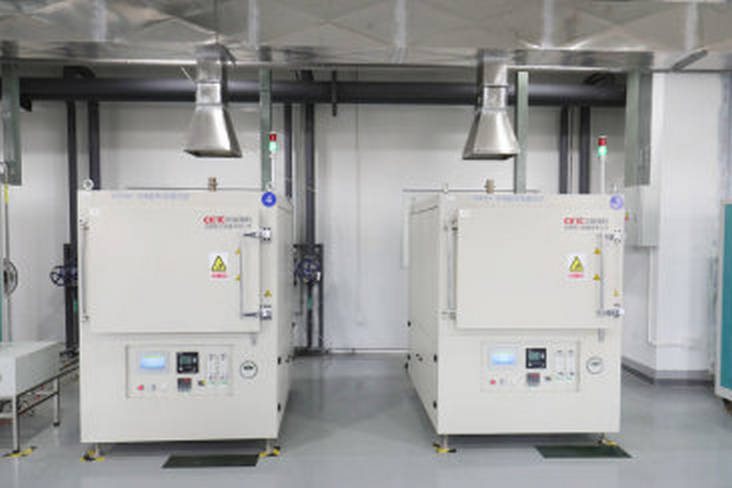


3. Pre-sintering (debinding)
The substrate blank made by tape casting contains a large amount of organic matter, which has a large internal porosity and low strength. If it is sintered directly, it will cause the substrate to shrink strongly and warp. In addition, it will cause the blanks to stick to each other during sintering, affecting the yield and thermal conductivity of the substrate. In order to prevent the above defects, pre-sintering in a nitrogen atmosphere furnace at 1100℃ and then sintering can improve the blank strength, reduce porosity, and obtain AlN substrate materials with high flatness and good performance.
4. High temperature sintering
After debinding, the aluminum nitride substrate will be sintered at high temperature. The sintering process of high thermal conductivity aluminum nitride substrate focuses on sintering method, addition of sintering aids, control of sintering atmosphere, etc.
Since AlN is a covalent compound with a small self-diffusion coefficient, sintering densification is very difficult. Rare earth metal oxides and alkaline earth metal oxides are usually used as sintering aids to promote sintering, but a sintering temperature of more than 1800°C is still required.
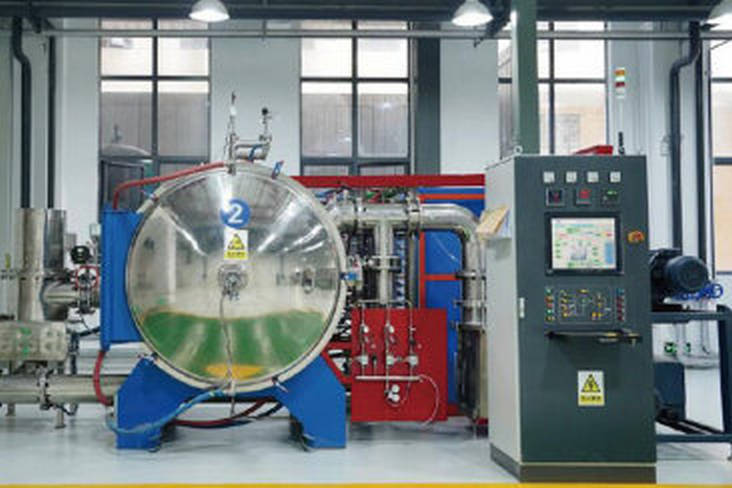
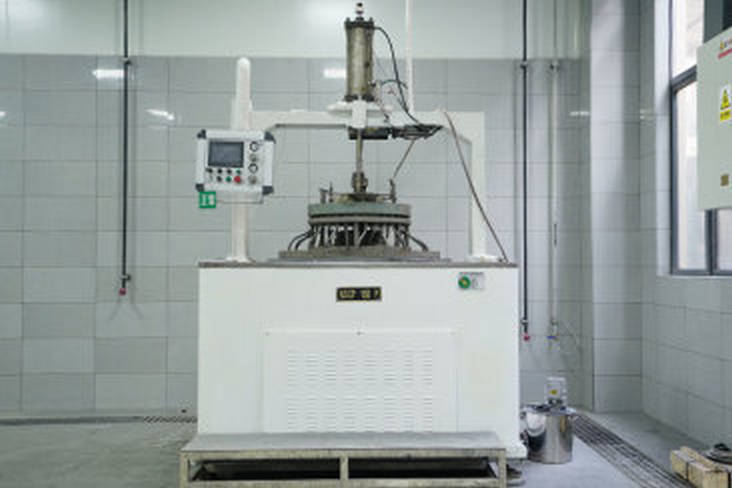


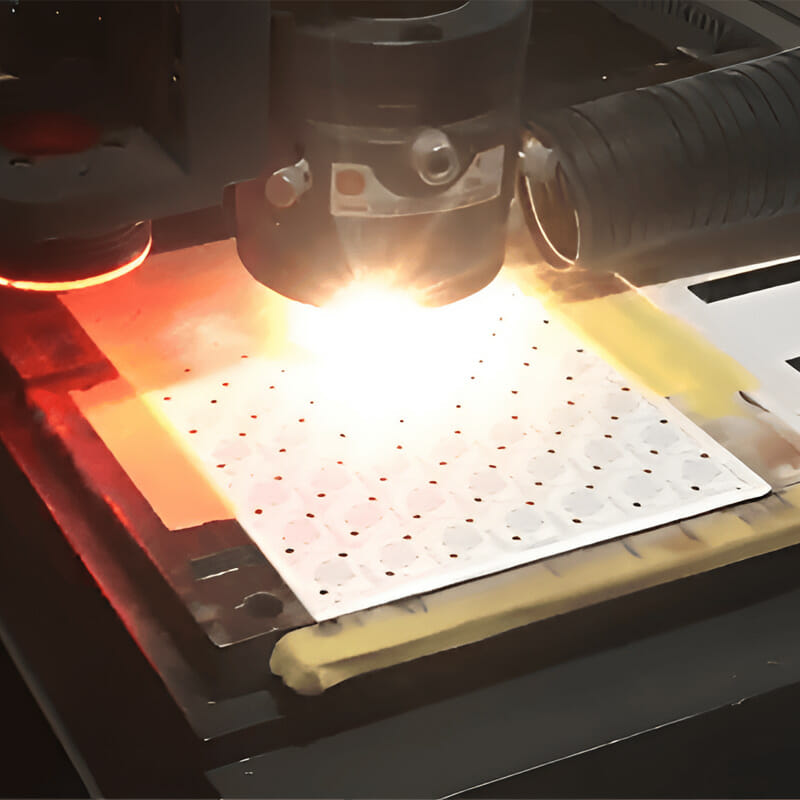
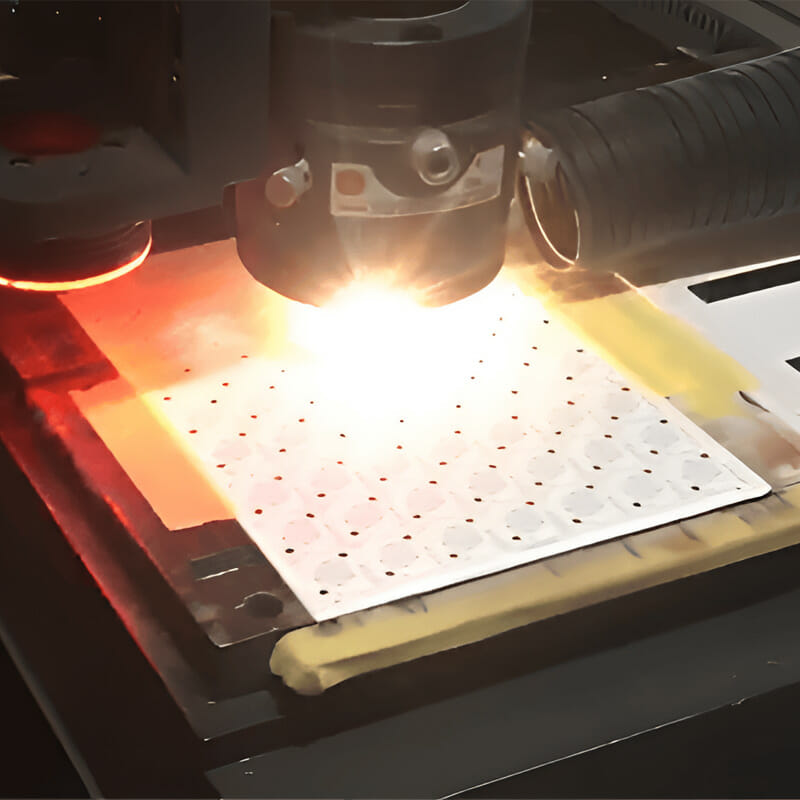
5. Aluminum Nitride Machining
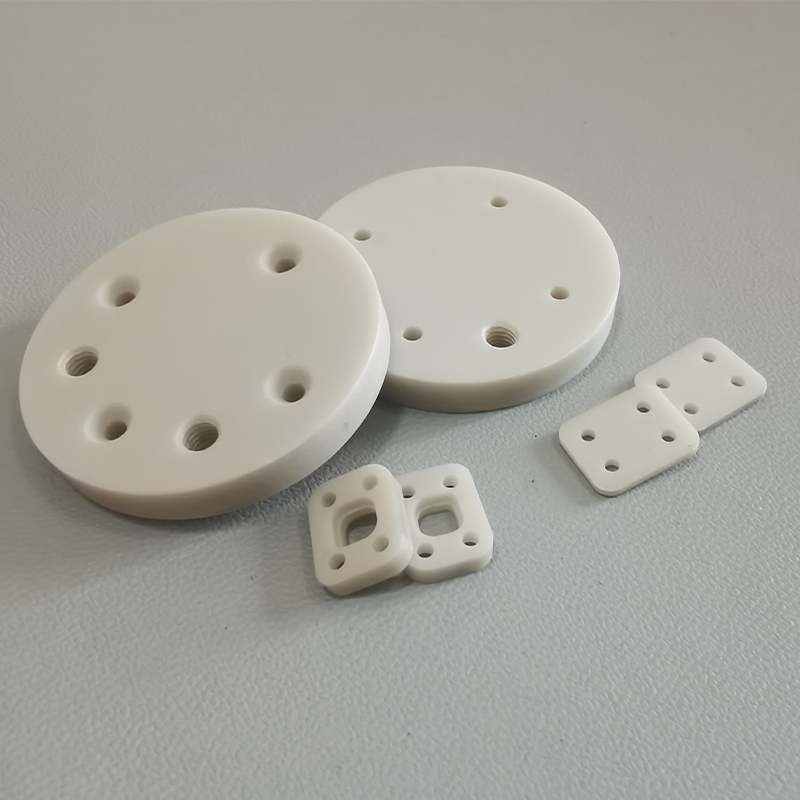
Aluminum nitride (AlN) sheets usually need to be precision machined after sintering to meet dimensional accuracy, surface finish and specific structural requirements. Due to its high hardness (1100-1200 HV), high brittleness, low fracture toughness, and high processing difficulty, highly specialized equipment is required for processing, such as end grinders, laser cutting machines, and other equipment.
To sum up
The production of aluminum nitride ceramic plates involves multiple links such as powder preparation, molding, sintering, and precision machining. The accuracy and control of each step directly affect the thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and reliability of the final product. With the continuous development of semiconductor packaging and high-power electronic applications, Great Ceramic's manufacturing process is also being continuously optimized to meet higher-end market demands.
Product Examples
Learn about ceramic substrate metallization